Introduction to the Internet
Definitions
The Internet: The Internet is simpler terms, essentially refers to the worldwide connection of various computer systems. The Internet communicates information in the form of data and media across a wide variety of interconnected devices. It is just a widely distributed network which as mentioned before comprises many interconnected devices. Computers utilise the internet to share information with each other as long as they have an Internet connection.

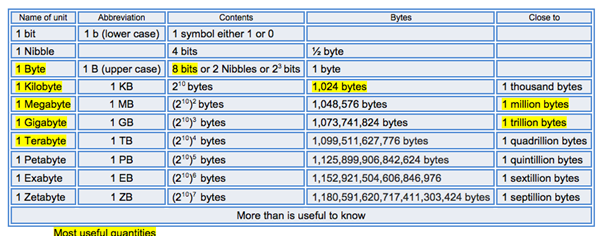
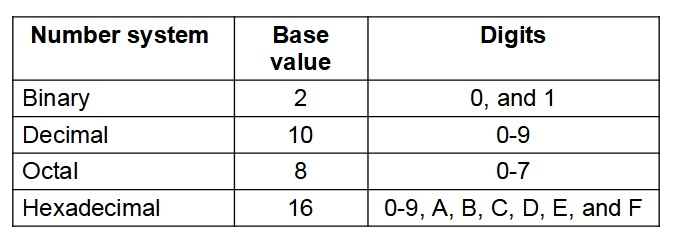
Bits, Bytes, Kilobytes, Megabytes: Bits and bytes are units of data transmitted over network connections. A bit is the smallest unit of data a computer can use and can only be represented by two possible states, 1 and 0. A byte is simply a fixed-length sequence of bits. There are 8 Bits in every Byte. The binary unit system is used to describe bigger numbers too. Eight bits are known as a byte. The binary unit system is as shown: 8 Bits = 1 byte(B), 1024 Bytes(B) = 1 Kilobytes(KB) = 1 Megabyte(MB). A kilobyte (KB) is a unit of digital information. It is equal to 1,024 bytes. A megabyte (MB) is a unit of digital information. It is equal to 1,024 kilobytes (KB), where 1 KB is equal to 1,024 bytes.
Binary: Binary is a number system that uses only zeros and ones. It is used by computers to store and process data because it can be easily represented using two states, such as on or off.
Computers use binary because it can be easily represented using two states, such as on or off.
These bits are strung together as different combinations of ones and zeroes, and they form a kind
of code. Your computer then rapidly processes this code and translates it into data, telling it what
to do.
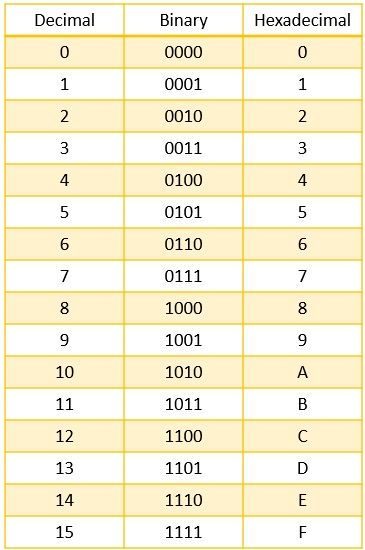
Decimal: Decimal, with reference to Computing, is the zero to nine numbering system. In computers, decimal arithmetic is used so that decimal fractional results of adding or subtracting values with a fixed length of their fractional part always are computed to this same length of precision. There are also decimal computers which can represent numbers and addresses in decimal as well as providing instructions to operate on those numbers and addresses directly in decimal, without conversion to a pure binary representation.
Ethernet, Fibre Optic Cable, Wireless:
Ethernet is basically a system to link a variety of computer systems to form a local area network or LAN. Here, protocols are established to control the transmission of information and to manage
the passing of this information. Fibre Optic cables are essentially cables that are made from one or more thin ductiles with a glass core through which light can be sent with very little interference
and loss. These specific types of cables are designed for long-distance communication,
performance based data networking and are also used in Telecommunications. Wireless if you think about it quite literally refers to having no wire and/or wires to connect various devices for various purposes. It uses electromagnetic, radio and/or microwave waves to send data through
the air. Wireless can also mean the various communication technologies present in our daily
world including radio and radiotelegraphy.

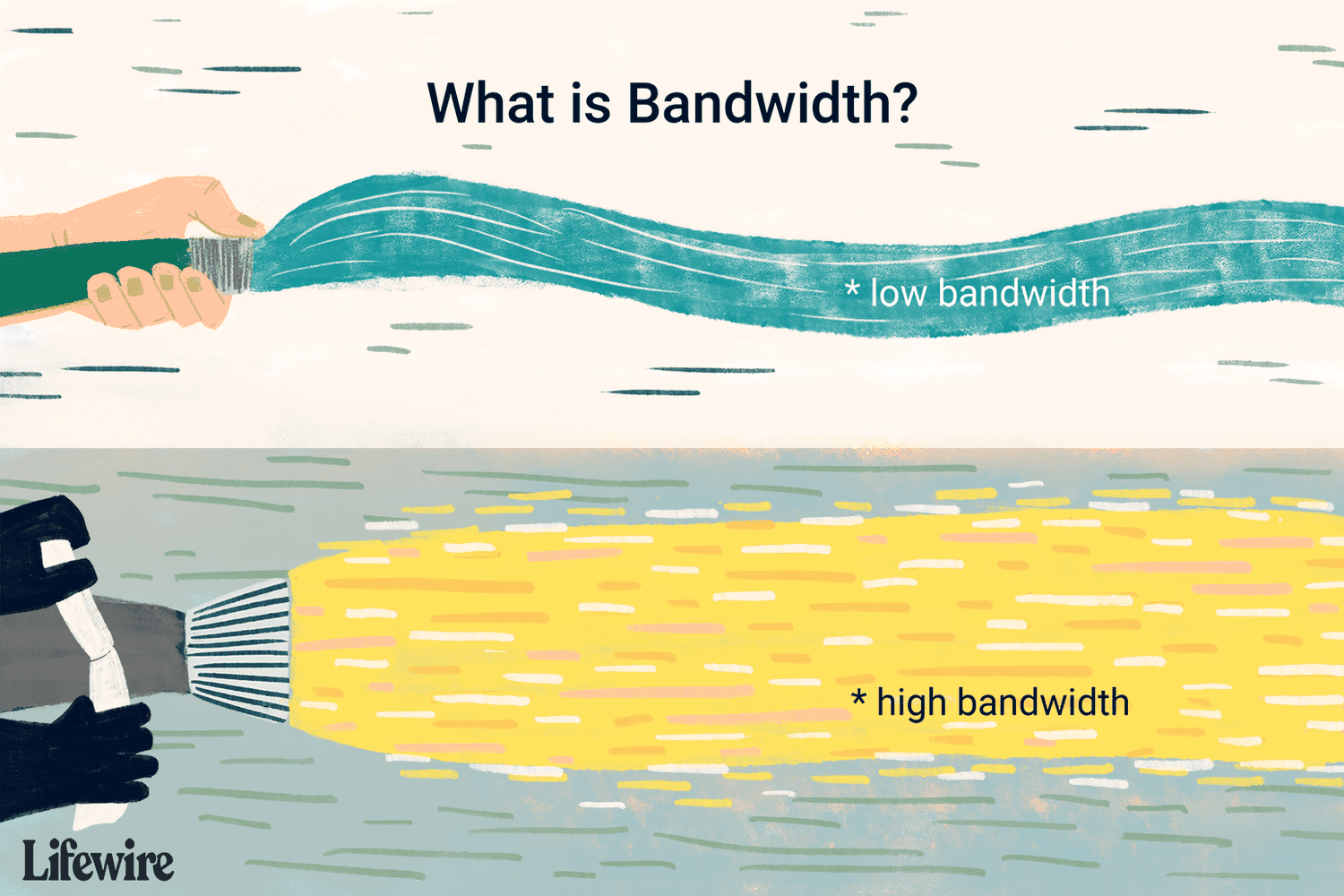
Bandwidth: The Bandwidth in simpler terms refers to the measure of the amount of data that
can be transmitted over a network over a specific period of time. With reference to computer networks, bandwidth refers to the capacity for data transmission of a particular electronics communication system. The higher the bandwidth, the more data that can be communicated over
a given period of time. The Bandwidth is usually expressed in bits per second(bps) or Bytes per second(Bps).
Analog: Although, one might think that analog means the showing of time with hands instead of
a digital representation, this is not what it is. Analog Internet means a type of internet connection that uses analog signals to communicate data. Analog signals are incessant and irregular that are able to display information such as electrical signals and sound waves.
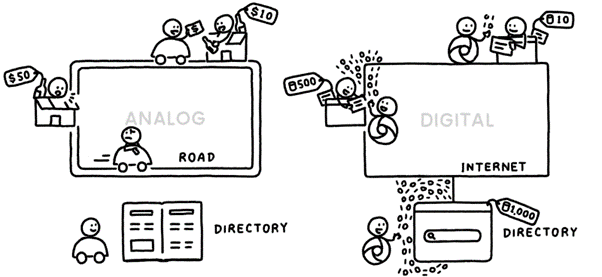
Digital: Digital Internet is basically a type of Internet connection that utilises digital signals to communicate data. These Digital signals are discrete and represent the information carried using binary digits. This essentially means that this information is represented in the form of bits, which are either on and off. As a result, they have extremely efficient and reliable transmission.
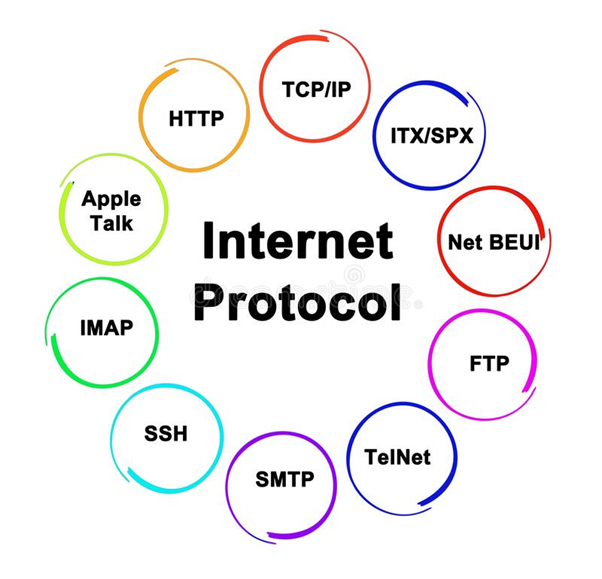
IP: Internet Protocol or Ip, is a set of rules that govern the format of data sent on the Internet or local area networks. It is responsible for routing data between various devices on a network. Here, each device on the network has an IP address which gives it access to communicate with other devices on the particular network. The Internet Protocol plays an imperative role and is a fundamental part of the Internet, as it enables communication between devices on a network. It is
a standardised way for all devices to communicate with each other to ensure that data can be transmitted reliably over lengthy distances.
IP Address: It is basically a unique label assigned to each individual device connected to a
specific computer network that uses the IP, or Internet Protocol for communication purposes.
IP addresses are meant to route the data between devices in a network. As mentioned before, each device on the network has a different IP address, which allows it to communicate with other
devices on the network. Moreover, the IP address is also used to correctly identify the origin and destination of these data packets as they are transmitted over the specific network. As of now, the Internet Protocol has two current iterations: IPv4 and IPv6. While IPv6 addresses are 128 bits
long, IPv4 addresses are 32 bits long. To resolve the lack of IPv4 addresses, the more recent IPv6 protocol was created.
