Cyber Security
Definitions
Virus: A Virus is a type of malicious code that can infect a computer or other device. A virus can typically replicate itself and spread to other devices by attaching itself to various files or programs.

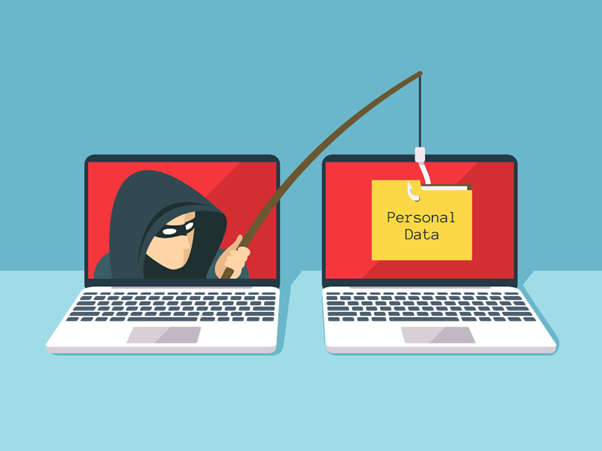
Phishing: Phishing is essentially a form of cybercrime where attackers trick people into revealing their sensitive and personal information. Phishing is mainly done by sending fake emails or messages that appear to be from a real company or source. The aim of these attacks is primarily
to get the credentials and sensitive information.

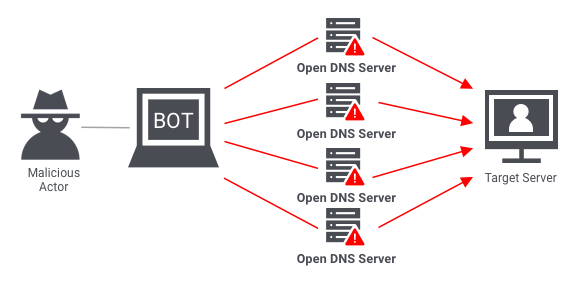
DDoS: DDoS or Distributed Denial of Service is basically a type of cyber attack where multiple affected devices are used to immerse a website with false web traffic(basically spamming requests). It aims to disrupt the functionality of a targeted server or network by overloading it with requests
in a form of internet traffic.
Anti virus software: Anti-virus software is basically a program that aims to protect an individual's device from malware like viruses and adware. It essentially scans the computer for threats and monitors the computer for any suspicious activity. If it does find out about malicious software, it will isolate it and remove it from the system. In simpler terms, An Anti-virus software provides real-time protection against virus attacks by running in the background.

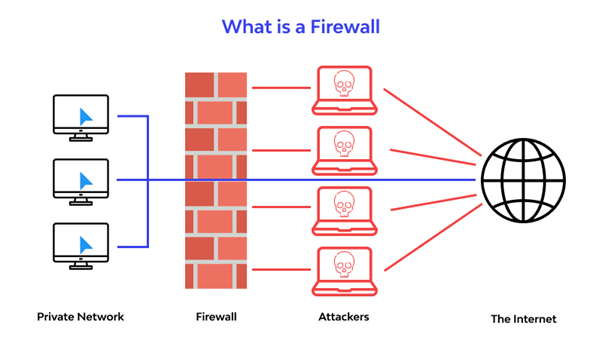
Firewall: Firewall is essentially a network security measure that monitors incoming and outgoing requests and decides whether to allow or block particular traffic based on a set of rules. It aims to establish a barrier between an internal network and incoming traffic from various other external sources in order to block and minimise malicious traffic to prevent unauthorised access to the specific network.